In Topeka, Kansas, a young African American girl named Linda Brown stood up for something that many other black girls would not have had the courage to face in 1951. Brown wanted to enter a white school due to the fact her black school was much farther away than the white school. Brown's father asked the NAACP to see if they would be able to assist their side of the argument, and help Brown to get into the school. The white side argued that the black schools were still profitable by some as some became succeessful coming out of high school. Brown and the NAACP tried to argue that the term "seperate but equal" was not applicable to minorities. Supreme Court Justice Earl Warren was the perfect man for Brown as he soon came to the conclusion that Brown was right. The minority position is no place for the term "seperate but equal", therefore it was deemed unconstitutional.
Thursday, March 31, 2016
Sunday, March 20, 2016
LAD #36: The Truman Doctrine
After WW2, a battle broke out without fighting between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R. Both nations sought to assert their power and their governmental influence over the developing countries around the world, communism vs capitalism. The Truman Doctrine concerns these developments in post-war Greece. After war-ravaged the country and sent it into a depression and overall disillusionment, the Soviets blockaded Grecian interests, preventing reconstruction and even staging a few terrorist attacks. Citing the inaction of Britain and the UN, Truman asserted the need of the United States to supply and finance Greece so that they would have the materials and the strength to rebuild their small nation. This was a way for Truman to try and stop the spread of communism. Also noted, was that backwards Turkey needed the aid of the democratic giant to spur on democracy and the will of the majority in a depleted post-war nation. As a result the U.S. would be the safeguard of freedom around the globe and the protector against the forces of communism. For this reason that Truman asked Congress to send a total of 750 million dollars and a contingency of American military servicemen and women to Greece and Turkey for reconstruction and modernization.
Sunday, March 6, 2016
LAD #35- FDR's Executive Order #9066
On the grounds that the success of WWII depended on the prevention of foreign espionage in America, FDR declares that the Secretary of War is authorized to construct military areas in which "any or all persons may be excluded", and he gave over to the Secretary the discretion to who should enter these areas. He states that the Secretary is authorized to provide food, transportation, shelter, and other accommodations for these groups. He also grants the Secretary the power to enforce compliance with these laws, and grants them the usage of Federal troops. This was brought along because of the panic after Pearl Harbor, and therefore created racial tensions between certain American groups and the Japanese Americans.
LAD #34- FDR's Declaration of War
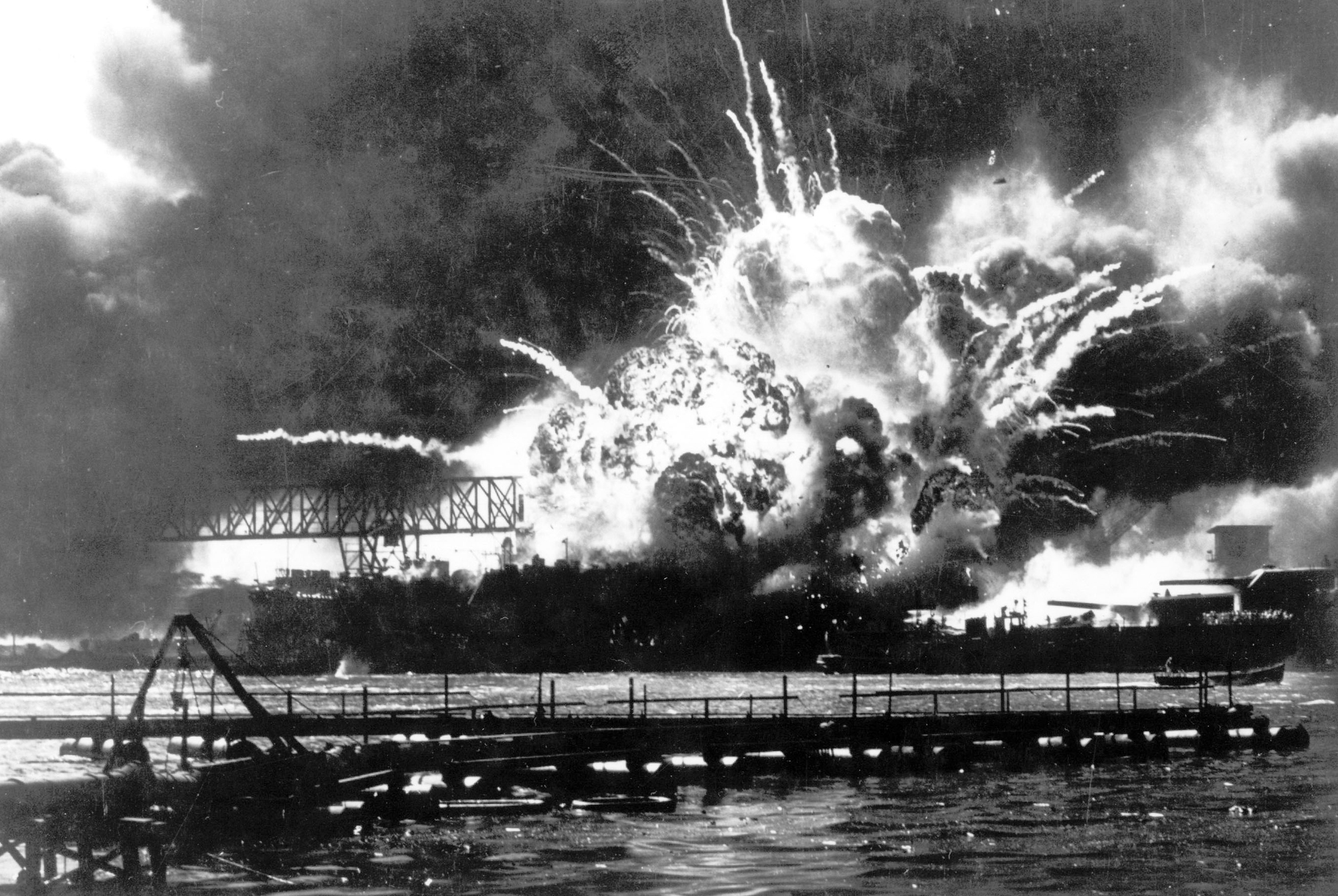
Pearl Harbor was attacked by the Japanese on December 7th, 1941. Roosevelt made a request to Congress, so America could declare war against Japan and protect itself. Roosevelt had confidence in two things; 1)the armed forces and 2)knowing that the people of the nation would come together to fight against the Japanese. Roosevelt asked Congress to think of what could happen if the Japanese were not punished for their harmful actions against America. Roosevelt insisted that the Japanese attack on Hawaii, along with all of their other aggressive acts recently, including Midway and Hong Kong, meant that they had no intent on a peace treaty with the U.S. In order to protect the American people, Roosevelt insisted that Congress declare war on the Japanese. This would not only bring upon the entrance of the U.S. into WWII, but also an end to the depression the U.S. had been plagued with because of the war it had to support.
Friday, March 4, 2016
LAD #33- FDR's First Inaugural Address
Franklin D. Roosevelt came into his presidency and the nation was at its all time low economically which became known as the Great Depression. Roosevelt realized the nation's trouble and acknowledges it. One of the things he states about fear is the nation should follow one thought, that "The only thing we have to fear is fear itself." His goal was to get people back working who had lost their jobs, and this would be accomplished by the direct employment of citizens by the government, which is a very progressive reform. Other ways included acting quickly and the teamwork of relief programs throughout the nation. This became known as the "New Deal," which would balance industries and work to strengthen currency flow. The New Deal created jobs and a program to help support the economy. His optimism in a time of depression, allowed for Americans to rally behind him and make it out of the Great Depression.
LAD #32- Kellogg Briand Peace Pact
The Kellogg Briand Peace Pact was signed by the United States, Japan, and parts of Europe in the late 1920's. This document recognized each nations duty to promote the welfare of mankind, it was something they had to do in order to ensure the best world to live in. The Pact stated that the renunciation of war should be used as a national policy to bring about peace and order. With the signing and passage of this pact, any nation that wished to declare war in pursuit of its own interest would be denied the benefits as decreed by the treaty. It was the hope of those who signed the treaty that future generations would follow this example. This was a major effort to keep nations out of war and to use diplomatic negotiations to solve their problems. The nations involved agreed that they would denounce the resulting causalities of war as a way to solve international disputes. They would also be open to consultation so long as they adhered to one another. The government of all nations would be recognized and follow the treaty, and all would possess a copy of the treaty and would notify one another if there were to be any alterations. This treaty was a way to ensure peace in the nation, but it did not work that long. By 1939, Europe was already in another war that captured the world along with it.
Sunday, February 7, 2016
LAD #31: President Wilson's 14 Points
President Wilson's 14 points outlined his beliefs of peace after the war, in this speech to Congress he proposed his ideas.
1) There should be no private meetings and all diplomacy should be peaceful and public.
2) Totally free navigation of the seas, there should be no difference in times of war and peace.
3) Trade should be equal between all nations agreeing to peace.
4) Nations should reduce their armories as low as possible, and used for domestic safety only.
5) Colonial claims should be unbiased, with the nation in mind.
6) All armies should be removed from Russia and allow it to develop in its own way.
7) Belgium should return to the independence it had before the war.
8) France will be completely free and retain control of Alsace-Lorraine.
9) Italians will continue to live in Italy and the borders will be based on nationality.
10) The people of Austria-Hungary will continue to develop in their own way.
11) Rumania, Serbia, Montenegro and other Balkan States will be free and establish their boundaries based on nationality, and they will work on their development.
12) The Turkish government will govern only Turkish people, and the other nationalities that were under Turkish rule, will become independent.
13) Poland will be independent with access to the sea.
14) The League of Nations will guarantee the freedoms and independence of all states in it.
1) There should be no private meetings and all diplomacy should be peaceful and public.
2) Totally free navigation of the seas, there should be no difference in times of war and peace.
3) Trade should be equal between all nations agreeing to peace.
4) Nations should reduce their armories as low as possible, and used for domestic safety only.
5) Colonial claims should be unbiased, with the nation in mind.
6) All armies should be removed from Russia and allow it to develop in its own way.
7) Belgium should return to the independence it had before the war.
8) France will be completely free and retain control of Alsace-Lorraine.
9) Italians will continue to live in Italy and the borders will be based on nationality.
10) The people of Austria-Hungary will continue to develop in their own way.
11) Rumania, Serbia, Montenegro and other Balkan States will be free and establish their boundaries based on nationality, and they will work on their development.
12) The Turkish government will govern only Turkish people, and the other nationalities that were under Turkish rule, will become independent.
13) Poland will be independent with access to the sea.
14) The League of Nations will guarantee the freedoms and independence of all states in it.
LAD #30- Schenck vs. US
In March of 1919, an American socialist, Charles Schenck faced the Supreme Court because of the government's suppression of rights, he wanted to peacefully resist the Conscription Act. Schenck was a radical, working during the war to get men to "draft dodge" and this hindrance of recruitment caused him to be charged with a violation of the Espionage Act. Progressives believed the draft was unconstitutional because the thirteenth amendment outlawed involuntary servitude. The government issued the Espionage Act during the war, and like the Sedition Act passed by Great Britain, suppressed the freedom of speech. The Act was an excuse to imprison socialists who posed a threat to the war and the government. Schenck made an appeal to the Supreme Court and in it his argument was that the Espionage Act was unconstitutional, violating his First Amendment rights. Justice Oliver Holmes articulated that when free speech presents a "clear and apparent danger", especially during war time. Schenck's anti war writings had presented a danger to the U.S. war effort and attempted to get people to be military insubordinates. The government was afraid. They were in a war and they thought Schenck's actions could cause disobedience so they unanimously voted against him. Therefore it was ruled free speech can be limited in wartime.
Sunday, January 17, 2016
LAD #29: Keating-Owen Child Labor Act
This act limited the number of hours children could work and stated that goods produced by child labor could not be sold over the states borders. This act stemmed from the muckrakers push for social reform. Due to this children under 16 could not work more than eight hours a day. This was later ruled unconstitutional because it restricted interstate commerce. Eventually a different child labor law was passed.
LAD #28: Wilson's First Inaugural
Woodrow Wilson starts off with discussing the governments change to favor the democratic party. He says the nation needs the democrats to change the nation- the nations point of view needs changing. The nation has good and bad aspects to it, which he lists. For example, the structure of the government is great, but bad things like human suffering brought on by the economic expansion of the nation were extremely negative effects of the government. According to Wilson, the government needs to fix its wrong doings brought on by industrialization. Issues that need resolving are the bank, the tariff, the agriculture and the industry. Natural resources are being exploited so they also need to be preserved. The governments job is to protect its people and they will do that with sanitation laws, pure food laws, and labor laws. He ends with "Today is not a day of triumph; it is a day of dedication."
LAD #27: The Clayton Anti-Trust Act
The Clayton Anti-Trust Act was passed to go along with the Sherman Anti-Trust Act. This was made to disband monopolies to protect workers. It also stopped exclusive sales contracts, corporate pooling's, and trust formations. It also stopped people from serving on the board of connecting companies and fines for unfair practices. It protected unions also, unlike the Sherman Anti-Trust Act.
LAD #26: MLK's 'I Have a Dream' Speech
The emancipation proclamation brought hope and joy to African America, but 100 years later, they are still hoping for the freedom they thought had been achieved. The nation said all men were created equal, but that statement has not been honored. So African-Americans went to the capital to demand the freedom and justice they deserve. The time for equality is now, the nation will not rest until equality has happened, but everyone must also not become people of hatred or violence. All brothers white and black, have their freedoms encased with one another. People must keep walking forward, as long as there is not equality, then African-Americans will not be satisfied. Do not despair though, changes will come. MLK then states that he has a dream, and says many of them including his children will "live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their heart." With the faith in these dreams, America will truly become a brotherhood. Let freedom ring.
Sunday, January 10, 2016
LAD #25: Dawes Severalty Act
In 1887, the president passed this act in order to take care of the Native Americans. This act created Indian Reservations, which would be on land that was unwanted by settlers. No reservation would be on land that was wanted by Americans. One quarter acre of land was allotted to each family, man over eighteen, and orphans, so they would have a space to live, and they could sell the land if they pleased. To a single person under eighteen one sixteenth of an acre land would be given. The president had the power to adjust this if he pleased, so they were not final. Reservation land could be decided by the Native Americans. Everyone who owned a share of the lands who benefit from it. Also if Native Americans wanted citizenship, it was offered to some tribes.
LAD #24: Jennings Bryan's Cross of Gold Speech
William Jennings Bryant starts by talking about the value of American workers, and the great country that America. To him we need more silver coins than gold and that would help our economy,it was hurting the farmers, a belief of the Populist Party and the Silver Democrats, who wanted silver also. Only wealthy men could use the silver that was cheaper than gold. The choice to do this would benefit the American public, and farmers are as important to the economy as big business men. Farmers could use this change in money to pay off the debts. He also believed in an income tax because it would benefit the people. Man should not be forced to spend his life for money, it should be more for the common man.
LAD #23: Populist Party Platform
The Populist Party, was a third party in the 1870's. The voting system is corrupt. Everywhere there is injustice and the public opinion has been silenced. Both parties have not done well and so the party of plain people came to be. Agriculture is a booming business, even though those who work in it do not see that money. Poverty should end and everyone should be righted. Declarations are as follows: Labors are permanent, wealth is for the people who create it, and people own the railroads not the other way around. Also flexible currency, coining of silver, circulation increase, graduated income tax, money in the hands of the people, banks keep money safe, telephone operated by the government for the people, land owned by aliens will be given to the people. The also pledged to resolve free ballot, tax on industry, support of pensions, unions, shorten work hours, abolish the pinkerton system, and opposition of corporations.
LAD #22: McKinley's War Messsage
Spain and Cuba had been fighting for many years, and McKinley finally talked to Congress about ending the war. He first talked about how each Cuban insurrection has cost the U.S. and as president he felt it was his job to address Congress. Trade with Cuba has suffered and the war ending soon is not likely. He had said previously that he would not annex Cuba, and rather he would be neutral. Therefore, McKinley formally proclaims America's neutrality and says that America will find other ways to help the Cubans. America will only formally enter the war if a few things happen. 1) If the war becomes miserable, and humanities suffer 2) Protecting the Cubans and giving them protection 3)If trade ends or destruction of property occurs 4)If our ships are attacked or our liberties are threatened. The USS Maine was destroyed, and due to this the war in Cuba must stop. It has hurt us economically and now it has hurt our navy physically. Now we await Congresses action, and hopefully this action helps our country
Pictured Above: William McKinley
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




.jpg)